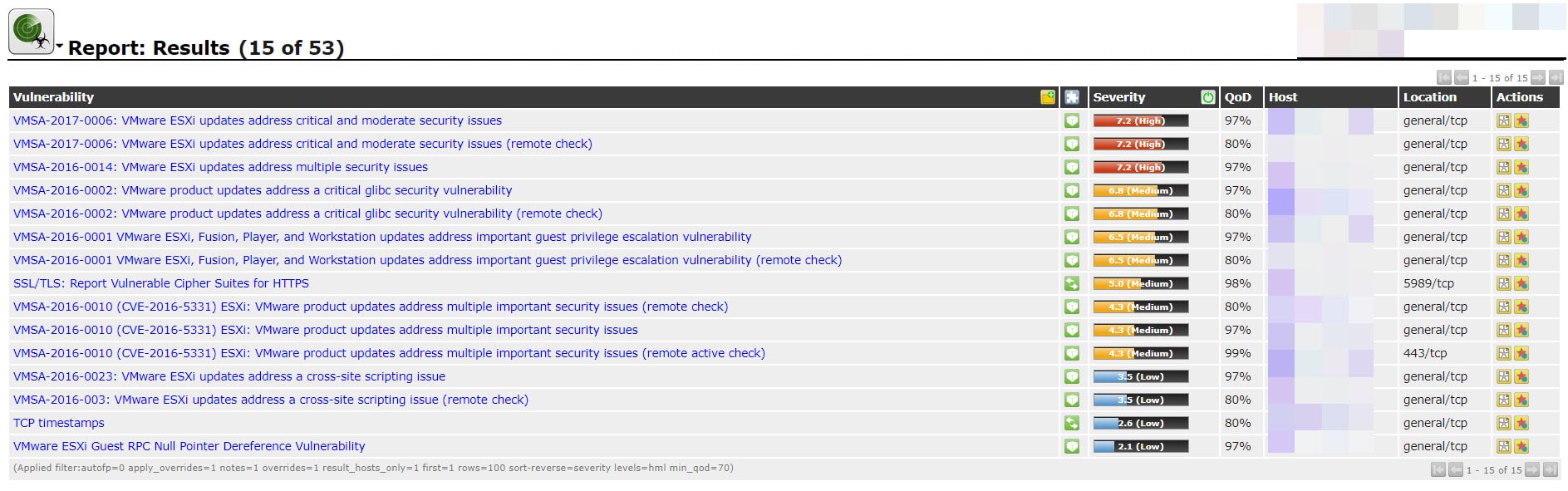
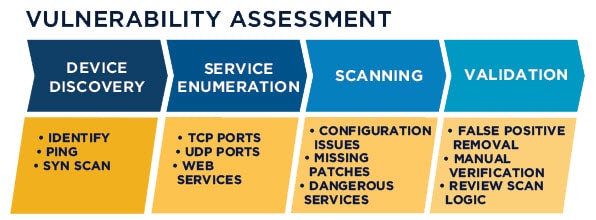
This is not a new features on last vSphere version but I went to write a post about that. We had to deploy different replication scenarios for our customers and some customers needs Point-In-Time Recovery (PiT) and The PiT solutions using VAIO actually so learning about the API is necessary for administrators.
The vSphere APIs for I/O Filtering (VAIO) were introduced in vSphere 6.0 Update 1. The VAIO framework and program were developed to provide VMware and partners the ability to insert filters for I/O into the data path of virtual machines. These “I/O Filters” enable VMware, and partners, to intercept and manipulate the I/O. This manipulation can provide open-ended data services, but thus far is limited to four use cases, two of which are currently exclusive to VMware and two which are open for partners. These use cases are: Replication, Caching, Quality of service (VMware only), Encryption (VMware only).



![[Review]: What's vSphere PMEM 10 HPE Persistent Memory](https://www.teimouri.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/08/hpe-pmem.jpg)

![[Review]: What's Remote Direct Memory Access(RDMA)? 14 Remote Direct Memory Access](https://www.teimouri.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/rdma_1.jpg)
![[Review]: VMware vSphere APIs for I/O Filtering (VAIO) 15 VMware vSphere APIs for I/O Filtering (VAIO)](https://www.teimouri.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/vmware_VAIO.jpg)
![[Review]: What's vSAN ReadyNode? 16 vSAN ReadyNode Configurator - vSAN OEM](https://www.teimouri.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/vsan_readynode_configurator_2.jpg)










