LINBIT (DRBD, LINSTOR): One of The Best Software Defined Storage Solutions
As the world’s leading provider of Software-Defined Storage, High Availability, and Disaster Recovery software, LINBIT (“DRBD, LINSTOR”) adds server clustering capabilities to any containerized, virtualized, or bare metal environment.
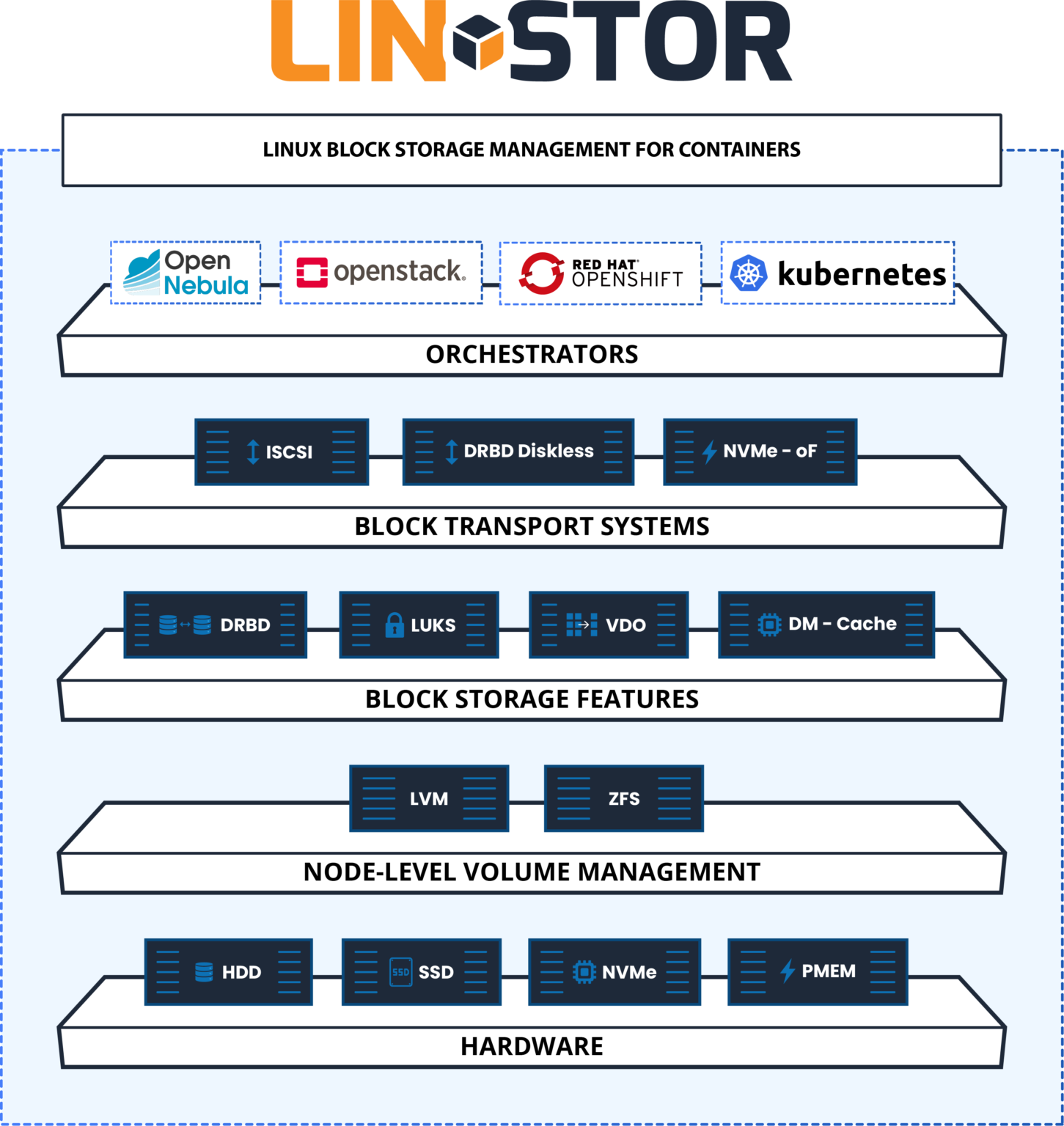
What’s LINSTOR?
With native integration to Kubernetes, LINSTOR makes building, running, and controlling block storage simple. LINSTOR is open-source software designed to manage block storage devices for large Linux server clusters. Its enterprise subscription LINBIT SDS, which includes DRBD, LINSTOR & Expert Support, is used for providing persistent Linux block storage for Kubernetes, OpenStack, OpenNebula, and OpenShift environments.
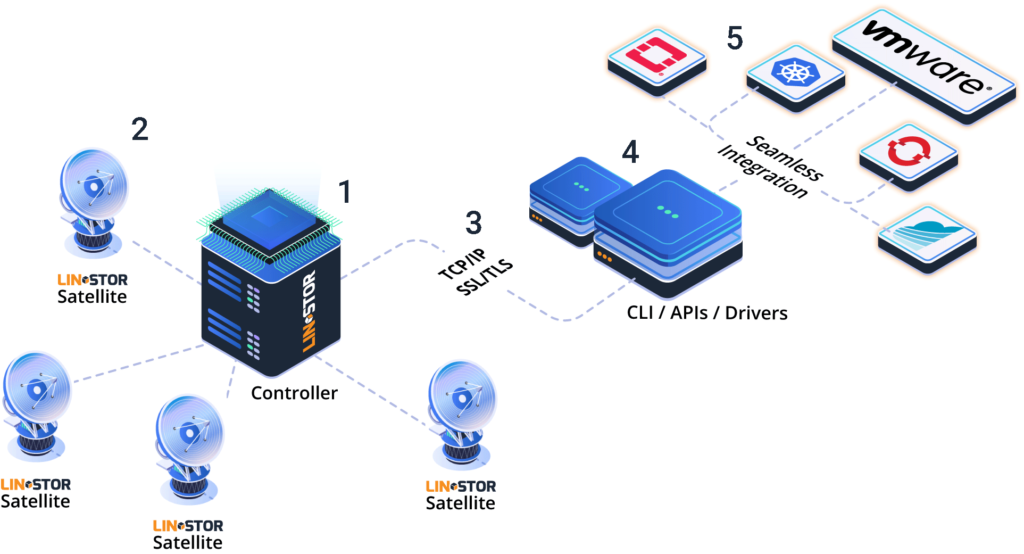
LINSTOR Components
The system consists of multiple server and client components.
- A controller manages the configuration of the LINSTOR cluster and all of its managed storage resources.
- The satellite component manages creation, modification and deletion of storage resources on each node that provides or uses storage resources managed by LINSTOR.
- All communication between components uses system’s own network protocol, based on TCP/IP network connections.
- The storage system can be managed by directly using a command line utility to interact with the active controller. Alternatively, users may integrate the system into the storage architecture of other software systems, such as Kubernetes.
- Seamless integration to various cloud environments with many additional software including Ha Controller, STORK, Kubectl Plugin, Operator
LINBIT SDS Features
Open Source
For the community, from the community.
Volume Management
Easily create, remove, modify volumes from CLI or API / Driver Support.
Multi – Tier Storage
Data can be stored on either HDD, SSD, NVME or PMEM. Live migration is possible between each other.
Geo-Clustering
Possibility to have multiple clusters in different geographical locations.
Data Deduplication
Data deduplication is one such technology that enables better utilisation of both storage devices and network bandwidth.
Low CPU & Memory Utilization
LINBIT SDS is performing better while consuming lowest CPU & memory in the market.
Ultra Fast Performance
World IOPS record is broken with LINBIT SDS + DRBD.
Wide Platform Support
Openshift, Opennebula, Openstack, Kubernetes, Docker, Hyper-v, Vmware, Proxmox
Unmatched In-Kernel Data Replication
Up to 32 replicated persistent volumes provided by DRBD.
Automatic Recovery
LINBIT SDS detects failures and automatically recovers from failed drives, network interfaces, failing switches, etc.
Data Locality
Each volume can be provisioned on local disks, or remote access can be achieved using Diskless, ISCSI, NFS, NVME-OF etc.
Scale-out, Distributed, Shared-nothing cluster architecture
High performance, scalability, availability, and reliability.
Data Integrity
In order to provide integrity, LINBIT SDS supports 3 synchronization methods which is; Variable-rate, Fixed-rate, Checksum-based.
Hyper-converged Infrastructure
LINBIT VSAN appliance gives you the ability to do Hyper-converged infrastructure. With the support of Hyper-converged, you can increase flexibility, simplify deployments, lower the costs. In short, do more with less.
Separated Data Path
Since LINBIT SDS components are not on the data path, you can easily upgrade and manage the entire cluster with ease.
iSCSI, NFS
Built-in HA (Highly Available), scale-out iSCSI target, and NFS server is managed by LINBIT SDS.
Multi-attach
The same volume may be attached to many servers/clients.
Multi Threaded Process
Ability to use multiple CPU cores in parallel in order to increase the performance per server.
Highspeed
Infiniband , RDMA and 10/40/56/100 Gbit Еthernet support.
Network, Redundancy and Load Balancing
Network redundancy can be archived by TCP/IP. With RDMA load balancing is possible.
LINBIT SDS Networking Protocol
(Diskless mode) developed for maximum throughput and lowest possible latency.
Online Volume Changes
Reconfiguration of the volume settings are possible without interruption.
REST API
Provide seamless integration, simple management, and high availability.
Shared Block Devices
Available on all of the client nodes, simultaneously accessible (Read only) and fully consistent.
Snapshots and Clones
Instantaneous, copy on write (CoW), snapshots and clones.
Storage Pools
Each pool may have a different set of drives. There may be a single pool or multiple pools per cluster. For best performance, SSD Pools can be created or HDD pools can be configured for big storage needs.
Cache Mechanism
Spinning drives need ssd caching for some scenarios, therefore LINBIT SDS supports that. (dmcache or bcache)
Templates
Automate volume creation and management. Resource groups, resource definitions are possible.
Thin Provisioning
Allows more storage visible to the users than is physically available on the system. Thin provisioning also allows snapshots and clones.
3 Types of replication
Synchronous, Asynchronous, semi-synchronous replication.
TRIM/ Discard
Trim/Discard are two names for the same feature: a request to a storage system, telling it that some data range is not being used anymore and can get recycled.
DRBD, Distributed Replicated Storage System
DRBD software is a distributed replicated storage system for the Linux platform. It is implemented as a kernel driver, several userspace management applications, and some shell scripts.
It is traditionally used in high availability (HA) computer clusters, but beginning with version 9, it can also be used to create larger software defined storage pools with a focus on cloud integration.
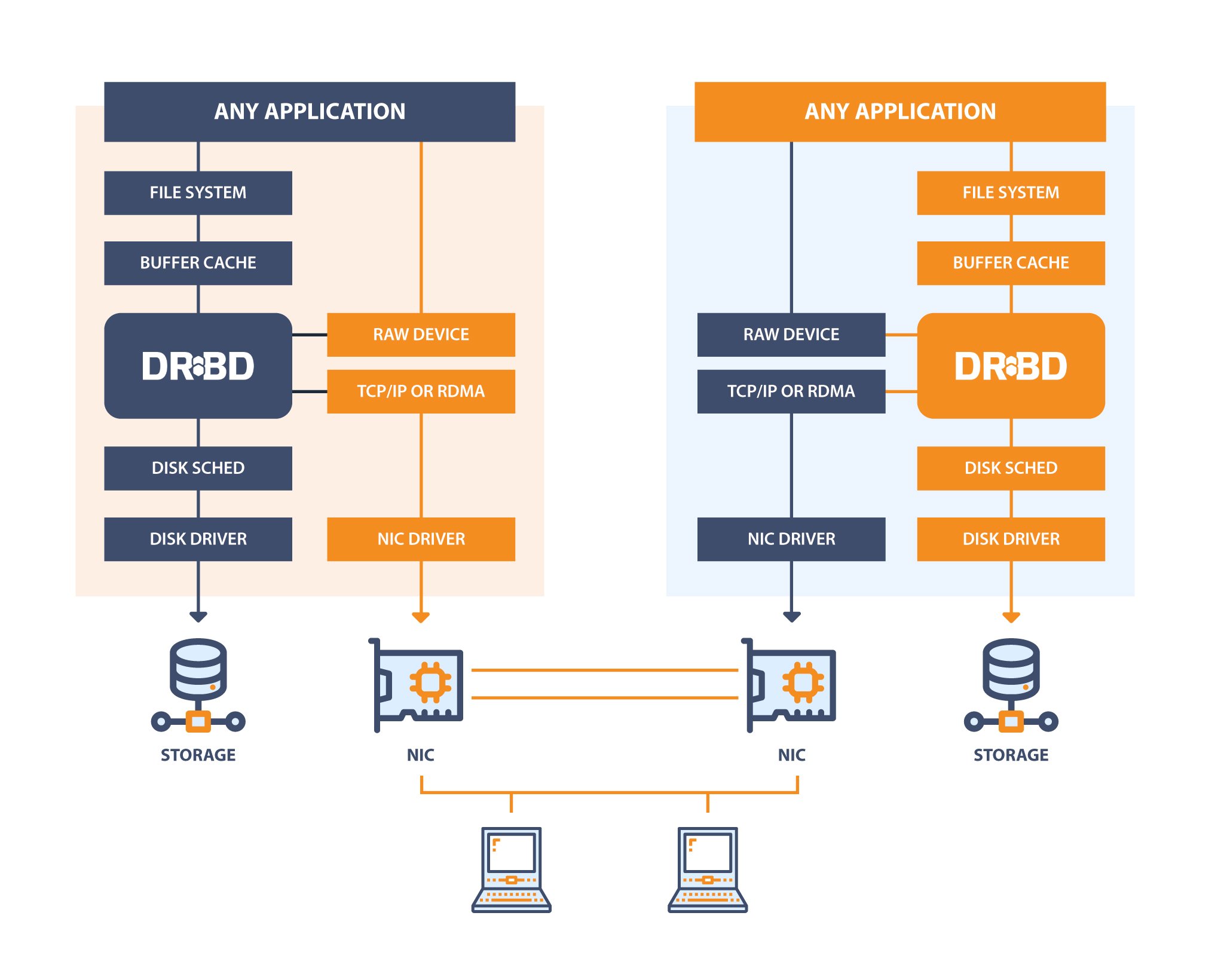
Linux Kernel Driver
The kernel driver presents virtual block devices to the system. It is an important building block of the DRBD. It reads and writes data to optional local backing devices.
Peer Nodes
The kernel driver mirrors data writes to one (or multiple) peer(s). In synchronous mode it will signal completion of a write request after it receives completion events from the local backing storage device and from the peer(s).
Data Plane
The illustration above shows the path the data takes within the kernel driver. Please note that the data path is very efficient. No user space components involved. Read requests can be carried out locally, not causing network traffic.
Utilities
drbdsetup
drbdsetup is the low level tool that interacts with the kernel driver. It manages the objects (resources, connections, devices, paths). It can modify all properties, and can dump the kernel driver’s active configuration. It displays status and status updates.
drbdmeta
drbdmeta is used to prepare meta-data on block devices before they can be used for DRBD. You can use it to dump and inspect this meta-data as well. It is comparable to mkfs or pvcreate.
drbdadm
drbdadm processes configuration declarative configuration files. Those files are identical on all nodes of an installation. drbdadm extracts the necessary information for the host it is invoked on.
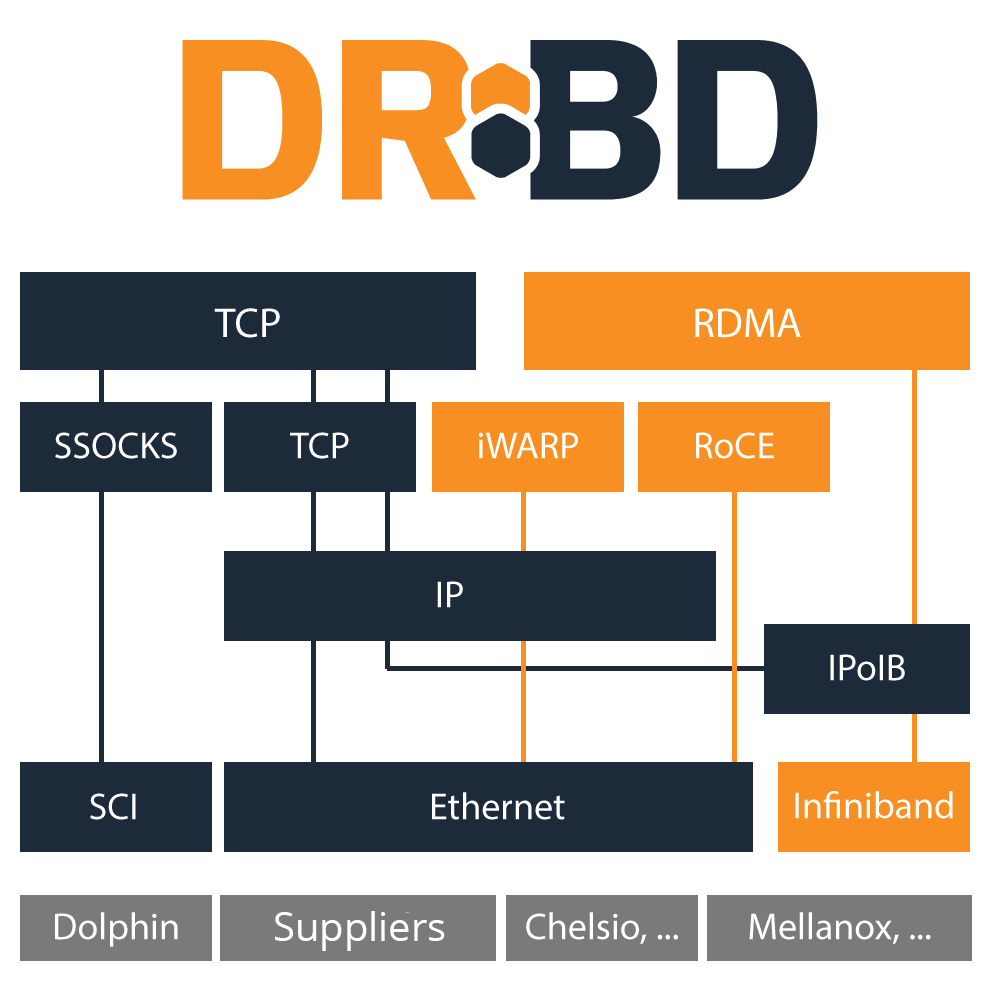
Networking Options
TCP/IP
TCP/IP is the natural choice. It is the protocol of the Internet. Usually it is used on top of ethernet hardware (NICs and switches) in the data center. While it is the lingua franca of the network it has started to become outdated and is not the best choice to achieve the highest possible performance.
RDMA/Verbs
Compared to TCP/IP a young alternative is RDMA. It requires NICs that are RDMA capable. It can run over InfiniBand networks, which come with their own cables and switches. It can run over enhanced ethernet (DCB) or on top of TCP/IP via an iWARP NIC. It is all about enhancing performance while reducing load on the CPUs of your machines.
WinDRBD, Highly Available Replicated Disk Drives for Windows
WinDRBD is the port of Linbit’s DRBD kernel driver and userspace utilities to the Microsoft Windows family of operating systems (Windows Server, Windows 10). It is based on the original source code, which makes it widely compatible with the Linux version. Most features that come with Linux version are also available on the Windows port. In addition, That can be used for booting a Windows client from a network resource.
Connecting a Windows WinDRBD resource with a Linux storage server enables you to benefit from features like LVM snapshots or zfs storage pools also on the Windows platforms.
Architecture
Technically, Windows driver consists of a thin Linux compatibility layer that emulates the Linux kernel APIs used by the driver for the Windows platform. Inside this layer, the original engine (with a few compiler-specific patches) is working.
To control the kernel driver the original user space utilities are used. They are ported using the CygWin POSIX emulation library which is also included in the Windows package (so there is no need to install CygWin alongside that).
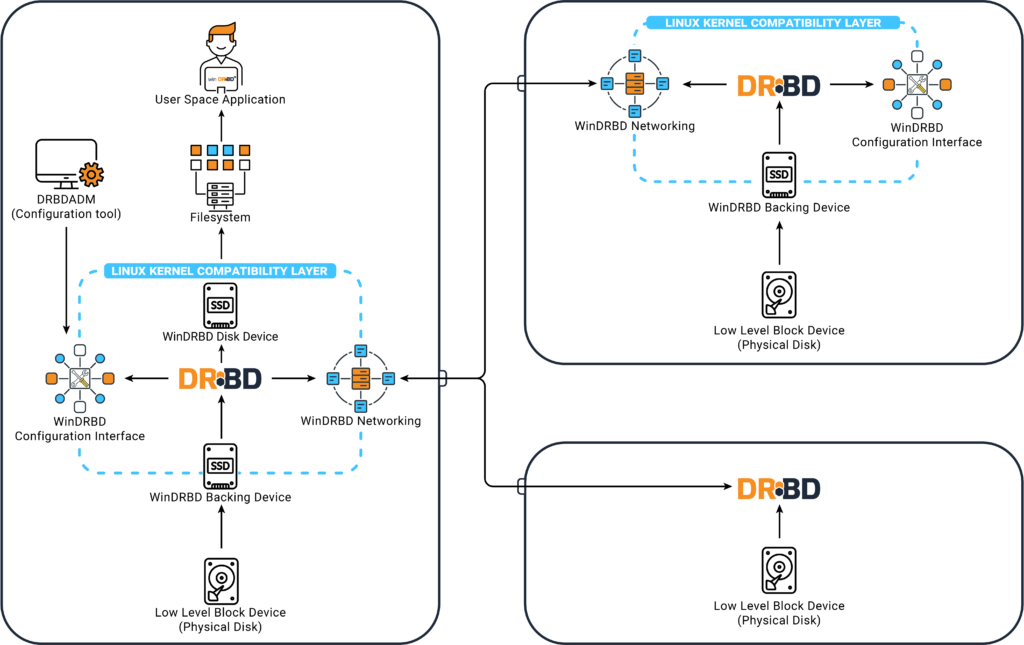
Use cases
Since Windows version is both application agnostic and file system agnostic many different use cases are imaginable:
- Implement highly available Windows servers. For example highly available MSSQL database servers
- Network boot: System volume (“C:”) over WinDRBD. To implement highly available centrally managed Windows clients WinDRBD here works as a replacement for iSCSI.
- Disaster recovery for Windows Clients. By using zfs / lvm snapshots on Linux peers, Windows storage can be rolled back in case of malware infection.
Proxy
Proxy helps DRBD in real-time replication with long distance. Proxy buffers the writes into memory, reducing bandwidth, latency and distance issues, ensuring your WAN latency isn’t a bottleneck.
Proxy basically provides 2 advantages. Data compression and cache operations. The biggest problem for disaster recovery solutions is that the connection between the two locations is cut off or the quality is low. In order to overcome these problems, we launched our Proxy product, which can work fully integrated with DRBD.
Proxy creates a buffer area between the two locations, allowing your data to be transferred smoothly in case of disconnection.
It also supports all compression standards in the industry, allowing you to carry a lot of data with less bandwidth, thus reducing your costs.
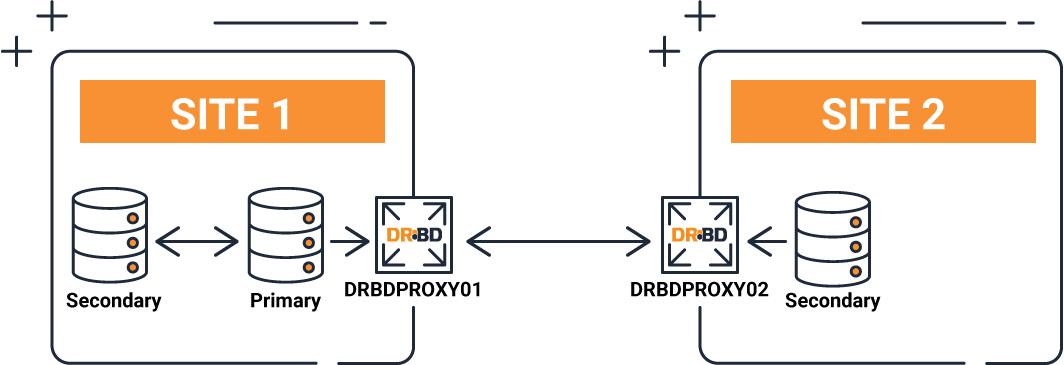
Off-site protection
Whether for regulatory compliance or peace of mind, an off-site replica of your data is designed to protect your important information during critical site outages, natural disasters, and other unfortunate circumstances. As a crucial part of your business continuity plan, LINBIT is dedicated to keeping your services applications up and running during even the most critical failures.
Common Use Cases
- Real time replica in Amazon AWS
- Connecting 2 or more company campuses
- Moving offices without downtime
- Off-site replicas for users in disaster prone areas
- Hosting providers who’s customers need a DR feature
Peace of mind
Unlike many proprietary vendors who make you purchase an expensive black box with licensed hardware and software and charge per machine Socket or per Gigabyte transferred, Proxy’s costs are per host/node. This makes Enterprise Level Disaster Recovery affordable for businesses of all sizes.
Near real-time replication
Proxy mitigates bandwidth, latency, and distance issues by buffering writes into memory ensuring that your WAN latency doesn’t become your disk throughput. Data is transferred as fast as your link can handle. Your organization can ensure Synchronous High Availability locally and Asynchronous Disaster Recovery replication off-site by using DRBD and Proxy together.
Cutting edge compression
To further mitigate bandwidth, latency, and distance constraints, Proxy includes native LZMA and LZ4 data compression options. For users looking to replicate an extensive amount of data using minimal CPU, LINBIT has partnered with AHA data compression hardware to minimize the CPU usage during data compression. For more information view our Technical Guide or contact us.
Not a backup
Our products are not backup solutions, they are real time replication solutions. We still recommend a sound snapshot technology is used along side our products. Real-time replication solutions like ours allow for minimal interruption during disasters.
Further Reading
What’s SDS (Software-Defined Storage) – Part 1 (Overview)
Ceph Storage Platform Alternatives in 2022
Parallel NFS (pNFS) – Part 1 (Introduction)
Veeam Backup & Replication – Bottleneck Analysis
External Links
LINSTOR – Storage Management For Containers (linbit.com)










