VMware vSphere 9.0 Revealed: Why Staying on Old Versions Could Destroy Performance
VMware vSphere has long been the foundation of enterprise virtualization. Now, with VMware vSphere 9.0, VMware is taking another leap forward to support modern workloads like AI/ML, GPU-intensive applications, hybrid cloud, and containerized environments.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn:
- What’s new in VMware vSphere 9.0
- Major feature enhancements and architectural changes
- Licensing changes and the move to subscription
- How vSphere 9 compares to vSphere 8 and 7
- The differences between VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) 9 and VMware Virtual Foundation (VVF) 9
- Supported and unsupported hardware from major vendors
- Real-world migration scenarios
- Troubleshooting FAQ
- Best practices for upgrading
This post is my first one after a few very difficult months, following the loss of my father. I hope I can get back on track and continue the path I was on. Let’s dive in.
Introduction to VMware vSphere 9.0
VMware vSphere 9.0 is the latest release of VMware’s industry-leading virtualization platform. It delivers improved performance, stronger security, and better management for both traditional VMs and next-gen workloads like containers and AI/ML models.
The vSphere 9 release continues VMware’s push to make your on-premises infrastructure more cloud-smart, integrated, and resilient.
Major New Features in VMware vSphere 9.0
Scalability Improvements
- VM Size Limits: Now up to 1,024 vCPUs and 24 TB RAM per VM on supported hardware.
- Clusters: Scale up to 128 hosts per cluster, supporting approximately 12,000 VMs.
- AI-driven DRS 2.0: Dynamic resource balancing powered by AI algorithms for improved performance and power efficiency.
Security Enhancements
- Native Key Provider Plus: Now FIPS 140-3 compliant for improved encryption.
- Confidential Computing: Supports AMD SEV-SNP and Intel TDX for stronger workload isolation.
- Immutable Snapshots: Protect against ransomware with tamper-proof VM snapshots.
- Policy-based Compliance: Built-in compliance templates for PCI-DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, and more.
AI & GPU Optimizations
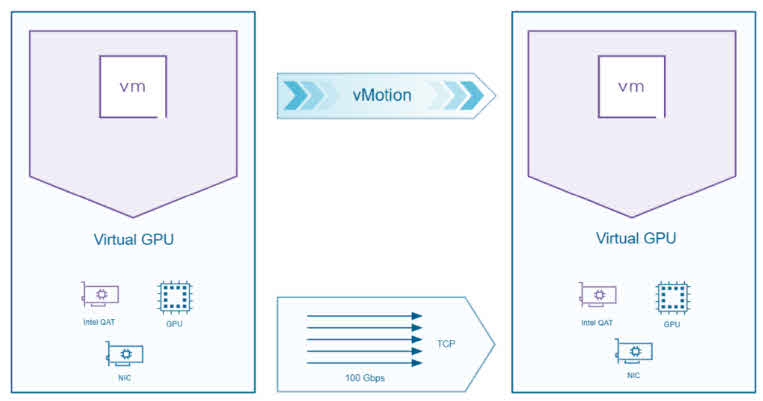
- vGPU Multi-Tenancy: Improved resource sharing for NVIDIA and AMD GPUs.
- AI/ML Zones: Designate specific zones within clusters for AI workloads.
- Tanzu AI Toolkit: Integrate Kubernetes-based AI pipelines seamlessly.
Lifecycle & Management
- Lifecycle Manager 2.0: Unified ESXi and firmware updates.
- Rolling vCenter Upgrades: Reduce downtime during upgrades.
- Enhanced HTML5 UI: Faster, mobile-friendly admin interface.
Licensing Changes in VMware vSphere 9
VMware vSphere is available in two standalone editions, VMware vSphere Standard and VMware vSphere Enterprise Plus, and is also included as a component in VMware Cloud Foundation and VMware vSphere Foundation. Note that vSphere Standard and vSphere Enterprise Plus are only available as versions up to the 8 Update 3 release. Currently, vSphere 9.0 features are only available as part of VMware vSphere Foundation 9.0 and VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0.
You can find more information on this document: vmw-datasheet-vsphere-product-line-comparison
Comparing VMware vSphere 9 to Previous Versions
Just like in previous releases, VMware vSphere 9.0 continues to build on its robust foundation. However, this version goes even further by offering significantly increased capacity and the ability to host larger and more complex workloads than ever before. In addition to these improvements, it introduces a variety of enhancements in both features and capabilities. With that in mind, let’s take a closer look at some of the key updates and what they mean for IT infrastructure and operations.
| Feature | vSphere 7 | vSphere 8 | vSphere 9 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max VM vCPUs | 768 | 896 | 1,024 |
| Max VM RAM | 12 TB | 16 TB | 24 TB |
| Max Hosts per Cluster | 96 | 96 | 128 |
| DRS Version | Classic | Enhanced | AI-driven |
| Confidential VMs | Limited | AMD SEV | AMD SEV-SNP & Intel TDX |
| Lifecycle Manager | Baseline Updates | Cluster Images | Images + Firmware |
| Licensing | Perpetual/Subscription | Hybrid | Subscription-first |
VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) 9 vs VMware Virtual Foundation (VVF) 9
VCF 9
- Full software-defined data center (SDDC) stack: vSphere, vSAN, NSX, and vRealize Suite.
- Built for hybrid cloud, advanced automation, and enterprise scale.
VVF 9 – (VMware vSphere 9.0)
- New, lightweight offering: vSphere 9 plus vSAN.
- Excludes NSX and full vRealize stack.
- Simpler and more cost-effective for edge, branch, or SMB environments.
| Aspect | VCF 9 | VVF 9 |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Private/hybrid cloud, enterprise scale | Branch, SMB, edge |
| Networking | NSX included | Optional or excluded |
| Automation | Full SDDC Manager | Basic vCenter only |
| Kubernetes | Fully integrated | Basic Tanzu |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Supported and Unsupported Hardware in VMware vSphere 9.0
Let’s review supported and unsupported hardware from some major vendors:
Supported Hardware
- Dell EMC: 15th/16th Generation PowerEdge servers.
- HPE: Gen10 Plus and Gen11 ProLiant.
- Lenovo: ThinkSystem SR650 V2, SR630 V2+.
- Cisco: UCS M6 and newer.
- Supermicro: X12 and X13 motherboards.
Unsupported or Deprecated
- BIOS-only servers (UEFI required).
- 1 GbE NICs with deprecated drivers.
- Older RAID controllers without VMW_PV drivers.
- CPUs lacking virtualization extensions.
Tip: Always update your BIOS and firmware before upgrading ESXi.
Realistic Migration Scenarios to VMware vSphere 9.0
Small Business (<5 Hosts)
- Validate all hardware on the VMware Compatibility Guide.
- Upgrade vCenter first.
- Use Lifecycle Manager for rolling upgrades.
- Consider moving to VVF 9 if you don’t need full NSX or advanced automation.
Mid-Market (~20 Hosts)
- Build a pilot cluster and test upgrades.
- Roll out cluster image–based upgrades.
- Use maintenance mode and rolling updates to minimize downtime.
- Upgrade VM hardware and VMware Tools after host upgrades.
Large Enterprise (50+ Hosts)
- Stage a test environment that mirrors production.
- Pilot upgrades on a subset of hosts.
- Use Cluster Image + Firmware upgrades via Lifecycle Manager 2.0.
- Automate with Ansible or vRealize Orchestrator.
- Evaluate moving to VCF 9 for full SDDC automation and hybrid cloud.
Troubleshooting FAQ
Q: Can I run older ESXi versions with vSphere 9 vCenter?
Yes, but only supported short-term. Upgrade vCenter first, then hosts.
Q: Why won’t my RAID controller show up?
It may lack supported drivers. Check the HCL and vendor firmware updates.
Q: Why are my old license keys invalid?
vSphere 9 requires subscription entitlements. Legacy perpetual keys won’t activate new features.
Q: The vCenter upgrade failed the pre-check.
Check plugin compatibility and resolve all warnings. Incompatible plugins commonly block upgrades.
Best Practices for a Smooth Upgrade to VMware vSphere 9.0
- Test upgrades in a lab environment.
- Upgrade vCenter before ESXi hosts.
- Use Cluster Image for consistent host configurations.
- Back up all workloads and configurations.
- Schedule maintenance windows with clear communication.
- Have rollback and recovery plans ready.
Conclusion
VMware vSphere 9.0 lays the groundwork for modern workloads with better performance, security, and cloud integration — but requires careful planning for licensing, hardware, and operations.
If you’re preparing to upgrade, it’s essential to assess your infrastructure, check compatibility, and plan a phased rollout.
Have you upgraded to vSphere 9.0?
Share your upgrade results or performance insights in the comments — your experience can help others!
FAQ
- What performance gains can I expect from vSphere 9.0?
➤ vSphere 9.0 delivers faster vMotion, improved resource scheduling, and up to 15% lower latency in benchmarks. - Is it risky to stay on older vSphere versions?
➤ Yes—older versions lack performance optimizations, may have unpatched vulnerabilities, and are unsupported in the future. - Can I upgrade directly from vSphere 7 to 9.0?
➤ Yes. VMware supports direct upgrades; however, a full backup and compatibility checks are recommended.
Further Reading
VMware vSAN Requirements and Best Practices: A Comprehensive Guide
Best Server Solutions for Oracle Database in Physical and Virtualization Environments
Silent Data Corruption: Understanding, Prevention, and Recovery
What’s Best Solution for Storing Oracle Database External Files in VMware vSphere?
Unlocking Database Management with VMware Data Services Manager: Features, Benefits, and Comparisons
External Links
What’s New in VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0 – VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) Blog




1 Response
[…] VMware vSphere 9.0 Revealed: Why Staying on Old Versions Could Destroy Performance […]