Networking is a key component of enterprise virtualization, and as data centers grow, it is imperative to manage network resources effectively and flexibly. VMware’s vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS) is a potent tool that allows for centralized management of networking configuration across ESXi hosts, and one of its key features is its management of network port bindings. There are two main types of bindings that are available with VDS: static and ephemeral. Virtualization administrators that want to optimize their environments must grasp the distinctions, benefits, and trade-offs between static and ephemeral port binding.
What is VMware vSphere Distributed Switch?
Before diving into the details of static and ephemeral bindings, let’s briefly review what a vSphere Distributed Switch (VDS) is and why it is important in modern virtualized data centers.
A vSphere Distributed Switch provides a single virtual switch that spans multiple ESXi hosts, allowing for centralized management of network settings such as VLANs, port groups, security policies, and network I/O controls. This capability improves network management efficiency and ensures consistency across the virtual environment.
Benefits of vSphere Distributed Switch:
- Centralized Management: Administrators can configure settings once and apply them across multiple hosts.
- Improved Network Visibility: VDS provides enhanced monitoring and troubleshooting tools, including NetFlow, Port Mirroring, and ERSPAN.
- Consistency: Ensures that network policies and configurations are uniform across the entire vSphere environment.
- Advanced Features: Supports advanced features like Load-Based Teaming (LBT), Network I/O Control (NIOC), and VLAN trunking, which may not be available with standard virtual switches.
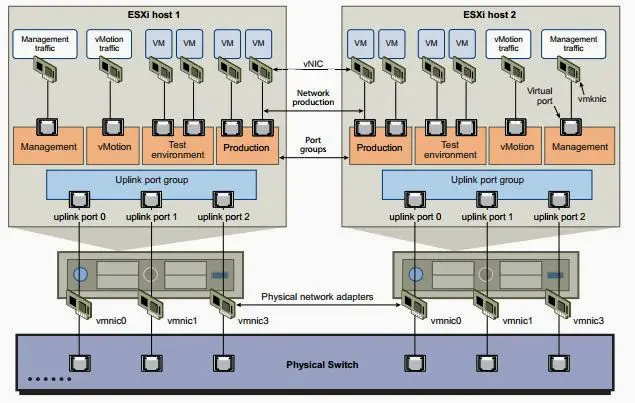
Understanding Port Bindings in vSphere Distributed Switch
In a vSphere Distributed Switch, each virtual machine (VM) is connected to the network via a virtual network adapter. This adapter connects to a port on the switch. How these ports are allocated and managed can be controlled by the type of port binding that is selected. Port binding defines when the port is assigned to a VM’s network adapter and how long that port assignment remains valid.
vSphere offers three different port binding types for distributed port groups:
- Static Binding
- Dynamic Binding (Deprecated)
- Ephemeral Binding
Since dynamic binding is deprecated and no longer recommended, this blog will focus primarily on static and ephemeral bindings.
Static Binding
Static binding is the default and most commonly used option in vSphere Distributed Switch configurations. When a port group uses static binding, a port on the VDS is assigned to a virtual machine’s network adapter when the VM is connected to the distributed port group. This binding remains fixed and persists across reboots and even vMotion events.
How Static Binding Works:
- Port Assignment: A port is reserved when the VM is powered on or when a network adapter is added to the VM. The port remains assigned to the VM’s network adapter for as long as the adapter exists.
- Persistent Connection: The port-to-VM binding is persistent, meaning the connection between the VM and its port is maintained across host reboots, VM migrations, and even after the VM is powered off.
- Early Binding: Ports are bound to VMs at the time of VM creation or when the VM is connected to the port group. This means that a port is allocated and reserved for a specific VM, even if the VM is not powered on.
Advantages of Static Binding:
- Predictability: Static binding ensures that a VM will always have a reserved port, which can be important for certain applications that require consistent network connectivity.
- Resiliency: The persistent nature of static binding makes it more resilient to disruptions such as host reboots or vMotion operations.
- Security: Since ports are statically assigned, administrators have better control over which VMs are allowed to connect to specific ports, reducing the potential for unauthorized access.
- Stability in Large Environments: In environments with large numbers of VMs and complex network configurations, static binding provides stability and reduces the risk of network misconfigurations.
Use Cases for Static Binding:
- Mission-Critical Applications: For applications that require guaranteed network connectivity, such as databases, static binding ensures that a network port will always be available.
- High Availability: In environments where high availability is a priority, static binding provides the stability and persistence needed to maintain consistent network connectivity.
- Environments with Frequent vMotion: Since static binding persists across vMotion operations, it is ideal for environments that use vMotion extensively for load balancing or maintenance tasks.
Potential Drawbacks of Static Binding:
- Port Exhaustion: Since ports are reserved even when a VM is powered off, there is a potential for port exhaustion, especially in environments with a large number of VMs. Administrators need to ensure that there are enough available ports to accommodate all VMs.
- Manual Configuration: In large environments, configuring static bindings manually can be time-consuming, especially if port group settings need to be changed frequently.
Ephemeral Binding
Ephemeral binding offers a more flexible and dynamic approach to port management. With ephemeral binding, ports are not statically assigned to VMs. Instead, ports are created and destroyed on-demand as VMs are connected or disconnected from the distributed port group.
How Ephemeral Binding Works:
- On-Demand Port Assignment: A port is dynamically created when a VM is powered on or connected to the distributed port group. The port is not persistent and is deleted when the VM is disconnected or powered off.
- Late Binding: Ports are assigned at runtime, meaning they are only created when a VM is actually powered on or connected to the port group. This allows for more flexible and dynamic port allocation.
- Temporary Nature: Since ephemeral ports are created and destroyed dynamically, they do not persist across reboots or vMotion events. If a VM is powered off or migrated, the ephemeral port is released.
Advantages of Ephemeral Binding:
- Flexibility: Ephemeral binding provides greater flexibility in environments where VMs are frequently created and deleted, such as in development or test environments.
- Avoids Port Exhaustion: Since ports are created and destroyed on-demand, ephemeral binding reduces the risk of port exhaustion, making it ideal for environments with a high churn rate of VMs.
- No Pre-Configuration Required: Ephemeral binding eliminates the need for pre-configuring port groups and assigning ports to VMs in advance. This can simplify the management of dynamic environments.
- Useful in Recovery Scenarios: Ephemeral binding can be particularly useful in recovery scenarios where distributed switch management or vCenter Server is unavailable, allowing administrators to bypass traditional binding and quickly recover VMs.
Use Cases for Ephemeral Binding:
- Development and Test Environments: In environments where VMs are frequently created, modified, and deleted, ephemeral binding allows for more dynamic management of network resources.
- Disaster Recovery: In scenarios where vCenter Server is unavailable, ephemeral binding enables administrators to power on VMs and establish network connectivity without relying on pre-existing port assignments.
- Short-Lived VMs: For VMs that are only needed for short periods of time, ephemeral binding ensures that ports are not unnecessarily reserved.
Potential Drawbacks of Ephemeral Binding:
- Reduced Predictability: Since ports are dynamically created and destroyed, network connectivity may not be as predictable or stable as with static binding, particularly in large, production environments.
- Overhead in Large Environments: While ephemeral binding is flexible, the overhead of dynamically creating and deleting ports can introduce complexity and potential performance issues in environments with a large number of VMs.
- Limited Features: Some advanced features of the vSphere Distributed Switch, such as Network I/O Control (NIOC), may not be fully supported with ephemeral port bindings.
Static vs. Ephemeral Binding: Key Differences
To better understand when to use static or ephemeral binding, let’s compare the key characteristics of each option:
| Feature | Static Binding | Ephemeral Binding |
|---|---|---|
| Port Assignment | Statically assigned when VM is connected to port group | Dynamically assigned when VM is powered on |
| Persistence | Persistent across reboots and vMotion events | Temporary; ports are created and destroyed on-demand |
| Port Allocation | Ports are pre-allocated and reserved | Ports are created as needed, no pre-allocation |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; requires manual configuration | Highly flexible; ideal for dynamic environments |
| Predictability | Predictable; ensures consistent network connectivity | Less predictable; ports are not persistent |
| Use Case | Mission-critical applications, high availability | Test environments, short-lived VMs, disaster recovery |
Best Practices for Choosing Between Static and Ephemeral Binding
Choosing between static and ephemeral binding depends on the specific requirements of your environment. Below are some best practices to consider when deciding which type of binding to use.
When to Use Static Binding:
- Production Environments: Static binding is ideal for production environments where stability, predictability, and consistency are key priorities.
- Applications with Persistent Network Requirements: Use static binding for VMs that run applications with strict network requirements, such as databases or mission-critical services.
- Environments with Limited vMotion Usage: In environments where VMs are not frequently migrated or deleted, static binding provides the persistence and stability needed for long-term operation.
When to Use Ephemeral Binding:
- Development and Test Environments: Ephemeral binding is well-suited for development, test, and lab environments where VMs are frequently created, modified, and deleted.
- Disaster Recovery Scenarios: In situations where vCenter Server or network management tools are temporarily unavailable, ephemeral binding allows for rapid recovery by dynamically creating ports as needed.
- High-Scale Dynamic Environments: For environments with a high turnover of VMs, such as cloud or containerized environments, ephemeral binding helps manage network resources efficiently without pre-allocating ports.
How to Configure Static and Ephemeral Binding in vSphere Distributed Switch
Configuring port binding in a vSphere Distributed Switch involves several steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to configure both static and ephemeral bindings.
Configuring Static Binding:
- Log in to vSphere Client: Open the vSphere Client and connect to your vCenter Server.
- Navigate to Distributed Switch: Go to the Networking and select the vSphere Distributed Switch you wish to configure.
- Edit Port Group Settings: Right-click on the port group you want to modify and select Edit Settings.
- Select Port Binding: In the Port Group settings, navigate to the General tab. Here, you will find the Port Binding option. Select Static Binding from the drop-down menu.
- Apply Changes: Click OK or Apply to save your changes. The port group is now configured to use static binding.
Configuring Ephemeral Binding:
- Log in to vSphere Client: Open the vSphere Client and connect to your vCenter Server.
- Navigate to Distributed Switch: Go to the Networking and select the vSphere Distributed Switch you wish to configure.
- Edit Port Group Settings: Right-click on the port group you want to modify and select Edit Settings.
- Select Port Binding: In the Port Group settings, navigate to the General tab. Here, you will find the Port Binding option. Select Ephemeral Binding from the drop-down menu.
- Apply Changes: Click OK or Apply to save your changes. The port group is now configured to use ephemeral binding.
Monitoring and Managing Network Bindings
Effective management of network bindings requires ongoing monitoring and adjustment. Here are some tips for monitoring and managing network bindings in your vSphere environment:
- Monitor Port Usage: Regularly check port utilization to ensure there are enough available ports for new VMs, especially in environments using static binding.
- Review Port Group Settings: Periodically review port group settings and adjust bindings based on changes in your environment, such as increased VM churn or new application requirements.
- Utilize vSphere Tools: Leverage vSphere’s built-in monitoring tools, such as NetFlow and Port Mirroring, to gain insights into network traffic and performance.
- Capacity Planning: For static binding environments, perform capacity planning to ensure that port availability matches the demands of your VM workload.
- Adjust Bindings as Needed: Based on monitoring data and changing requirements, adjust port bindings to optimize network performance and resource utilization.
Conclusion
In the world of VMware vSphere Distributed Switches, the choice between static and ephemeral port binding can significantly impact network performance, resource management, and operational flexibility. Static binding offers stability and predictability, making it ideal for production environments and applications with consistent network requirements. On the other hand, ephemeral binding provides flexibility and efficiency, which is beneficial for dynamic, high-turnover environments such as development or test labs.
By understanding the differences between static and ephemeral bindings and following best practices for configuration and management, virtualization administrators can ensure that their network infrastructure supports their organization’s needs effectively. Whether managing a large-scale data center or a dynamic cloud environment, selecting the appropriate port binding strategy is key to achieving optimal network performance and reliability.
For more insights on VMware vSphere Distributed Switches and network management, stay tuned to our blog and subscribe to our newsletter. If you have any questions or need further assistance, feel free to reach out to our community or support team.
External Links
vSphere Distributed Switch | VM Networking | VMware
Static (non-ephemeral) or ephemeral port binding on a vSphere Distributed Switch (broadcom.com)
Further Reading
[Review]: What’s Remote Direct Memory Access(RDMA)?
[Review]: Packet Drop vs Packet Loss – Linux
Using Network Partitioning (NPAR) in VMware ESXi
A Deep Dive into VMware vSphere vMotion Application Notification: Keeping Applications in the Loop